前言
回顾上期的内容,编写了 effect 中的调度器,主要修改了 effect.ts 文件。在预览之前的代码的时候会发现一些优化的地方。
在 vue 代码的需求编辑中,会遇到这样一个例子。例如一个人的姓名分为姓和名,那么我希望在页面上打印出这个人的姓+名,而且在姓或者名改变的时候,页面渲染也会改变。那么就用到了 vue 的 computed 来进行操作。旧版的 vue2 中 computed 是基于 watcher 实现的。vue3 则是基于 effect 来实现。另外 vue3 中的 computed 写法叫组合式 API,而 vue2 是拿 data 中的属性来编写 computed 中的属性,这种叫选项式 API(option)。具体的 vue3 写法如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| const { effect, reactive, computed } = VueReactivity;
let target = { firstName: "张", lastName: "四" };
const state = reactive(target);
let app = document.getElementById("app");
const fullName = computed(() => {
console.log("runner");
return state.firstName + state.lastName;
});
effect(() => {
return (app.innerHTML = fullName.value);
});
setTimeout(() => {
state.firstName = "王";
}, 1000);
|
也可以写成如下的方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| const fullName = computed({
get() {
console.log("runner");
return state.firstName + state.lastName;
},
set() {},
});
fullName.value;
fullName.value;
fullName.value;
|
并且在多次访问 value 的时候,如果值未改变就不触发运行,也就是说带有一个缓存的功能。
baseHandle 功能优化
在给属性包裹一层代理的时候,如果对象的属性还是一个对象之类的属性,那么返回的不应该只是这个值,而应该是这个对象代理之后的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
let res = Reflect.get(target, key, recevier);
if (isObject(res)) {
return reactive(res);
}
return res;
|
编写 computed 功能
对着上面的官方用法,知道如果只有一个函数的话,那就是这个函数默认为 get,还可以有一个对象的写法,那就是将用户的 set 和 get 赋值上去。
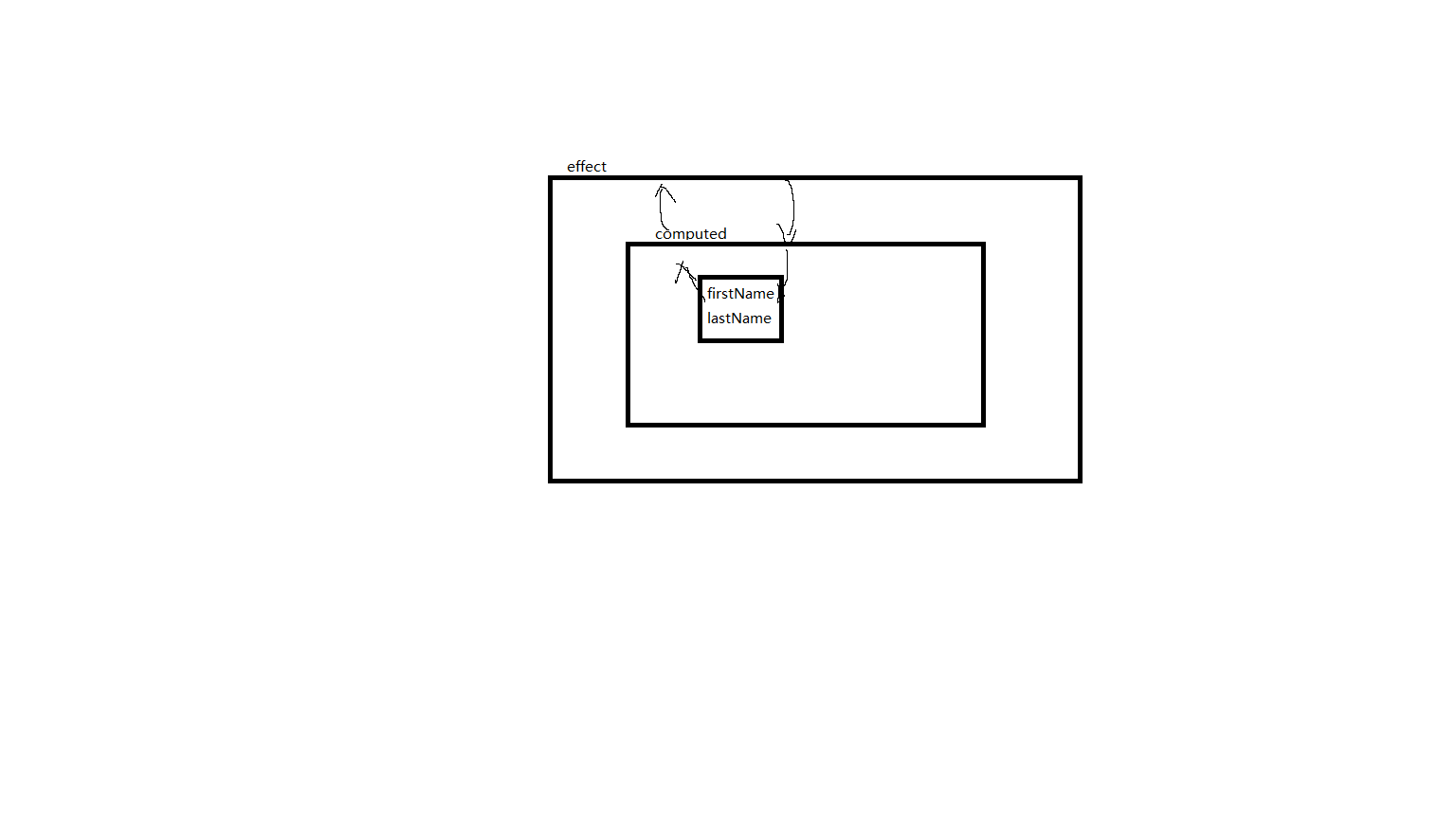
另外还 effect 中渲染了 computed 抛出的值,然后这个值改变了,也触发了 effect 的 run,让他重新渲染,这说明 computed 是记录了 effect 的依赖的。
上文说过 computed 是基于 effect,实际上它和 effect 基本相等。那么就出现了 effect 包裹了 effect 这种写法。
![48a2d11a721ffa60acaac.png]()
也就是这样传递着改变的信息,来触发页面渲染。
第一步创建 computed.ts 基础
判断传递过来的式函数还是对象,然后就获取传递的 get 和 set
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| export const computed = (getterOrOptions) => {
let onlyGetter = isFunction(getterOrOptions);
let getter: Function, setter: Function;
if (onlyGetter) {
getter = getterOrOptions;
setter = () => {
console.warn("no set");
};
} else {
getter = getterOrOptions.get;
setter = getterOrOptions.set;
}
return new ComputedRefImpl(getter, setter);
};
|
编写 ComputedRefImpl 类
这个类主要的操作是
第一个赃值检测,就是 value 值多次 get,然后值还没改变。
第二个是搜集 effect,这样值更新通知对应的 effect 进行用户的函数回调
第三个如果不是赃值,那就运行调度函数,就是用户的操作函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class ComputedRefImpl {
public effect: ReactiveEffect;
public _dirty: boolean = true;
public __v_isReadonly: boolean = true;
public __v_isRef: boolean = true;
public _value: any;
public dep = new Set();
constructor(public getter: Function, public setter: Function) {
this.effect = new ReactiveEffect(getter, () => {
if (!this._dirty) {
this._dirty = true;
triggerEffect(this.dep);
}
});
}
get value() {
trackEffect(this.dep);
if (this._dirty) {
this._dirty = false;
this._value = this.effect.run();
}
return this._value;
}
set value(newValue) {
this.setter(newValue);
}
}
|
上面代码中的 triggerEffect 和 trackEffect 是对之前的 effect 代码做了一个函数功能分离。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
export function trackEffect(dep: any) {
if (activeEffect) {
let shouldTrack = !dep.has(activeEffect);
if (shouldTrack) {
dep.add(activeEffect);
activeEffect.deps.push(dep);
}
}
}
export function triggerEffect(effects) {
effects = new Set(effects);
effects.forEach((effect) => {
if (activeEffect !== effect) {
if (effect.schedule) {
effect.schedule();
} else {
effect.run();
}
}
});
}
|
结尾
经过上面的代码编写之后就能得到一个自己的 computed 函数,可以试验下,发现能得到相应的效果
1
| git:[@github/MicroMatrixOrg/vue3-plan/tree/add-computed]
|